Notice Past And Past Participle Form V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 Form of Notice
Have you ever paused to think about the different forms of a simple word like “notice”? Whether you’re learning English or polishing your grammar skills, understanding verb forms is crucial.
The word “notice” might seem straightforward, but it transforms intriguingly across its various forms: V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5. Imagine mastering these forms and instantly improving your communication skills. Picture yourself confidently using past and past participle forms without second-guessing.
This guide will unravel these verb forms, making it easy for you to grasp and apply them. Curious about how this can enhance your language skills? Keep reading, and you’ll discover the secrets of the verb “notice” that will elevate your English proficiency.
Credit: www.youtube.com
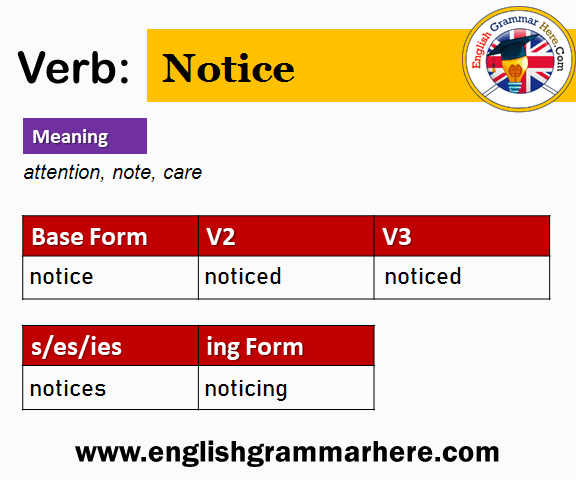
Basic Forms Of Notice
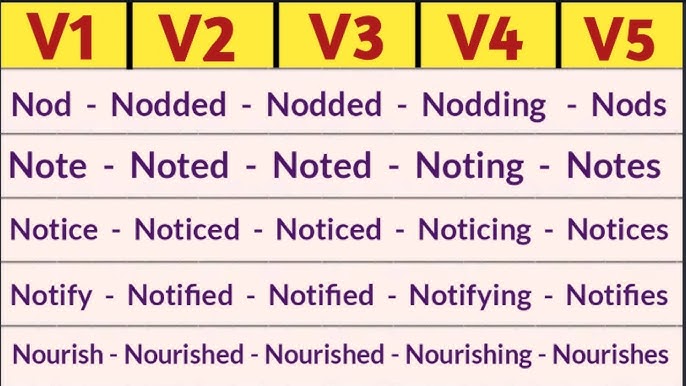
Noticeis a simple word. It means to see or hear something. In grammar, it has different forms. The base formis “notice.” The past formis “noticed.” The past participleis also “noticed.” The present participleis “noticing.”
Here is a table with these forms:
| Verb Form | Notice |
|---|---|
| Base Form (V1) | notice |
| Past Form (V2) | noticed |
| Past Participle (V3) | noticed |
| Present Participle (V4) | noticing |
| Third Person Singular (V5) | notices |
These forms help in making sentences. They change with time.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Conjugation Patterns
The verb “notice” changes its form in different tenses. In the present tense, it is “notice.” Past tense is “noticed.” The verb becomes “noticed” in past participle form too. This form is used with “have” or “had.” For example, “I have noticed.” In the present participle, it turns to “noticing.” This form is used for ongoing actions. For example, “I am noticing.” Lastly, the verb remains “notice” in the simple form.
Here is a summary:
| Form | Example |
|---|---|
| V1 (Base) | notice |
| V2 (Past) | noticed |
| V3 (Past Participle) | noticed |
| V4 (Present Participle) | noticing |
| V5 (Simple) | notice |
Usage In Sentences
Noticemeans to see or become aware of something. In its base form, it is used when talking about something happening now. For example, “I notice the birds singing.” In the past, “noticed” tells us the action has already happened. “She noticed the change in weather.” The past participle form is also “noticed” and is used with helping verbs like ‘have’ or ‘had.’ “They have noticed the mistake.” In the continuous form, “noticing” shows the action is ongoing. “I am noticing new things every day.” The future form “will notice” talks about what will happen. “You will notice the difference soon.”
Kids notice things quickly. Parents noticed the mess. Teachers have noticed the student’s progress. Artists are noticing details in their work. Scientists will notice new patterns.

Credit: englishstudyhere.com
Conclusion
Mastering the forms of “notice” helps in effective communication. Remember V1 is “notice,” V2 is “noticed,” and V3 is “noticed. ” V4, the continuous form, is “noticing. ” V5, the perfect form, remains “noticed. ” These forms guide proper tense usage.
Practice them regularly to boost your language skills. Use these forms to express ideas clearly. English language learning becomes simpler with these tools. Understanding these forms aids in writing and speaking. Stay consistent in practice. Your grasp on language will improve.
Keep learning, and watch your confidence grow.