Gag Past And Past Participle Form V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 Form of Gag
Have you ever found yourself puzzled by the different forms of a verb, especially when you’re trying to use it correctly in a sentence? You’re not alone.
Understanding the past and past participle forms of verbs can be a challenge, but it doesn’t have to be. If you’re curious about the verb “gag” and how it transforms through its various forms—V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5—you’re in the right place.
Mastering these forms not only enhances your grammar skills but also boosts your confidence in communication. Dive into this article and discover the simple tricks to mastering the verb “gag” in all its forms. You’ll find that using them correctly can make a significant difference in the clarity and impact of your writing and speaking. Let’s unlock the mystery together and make your language skills even sharper.
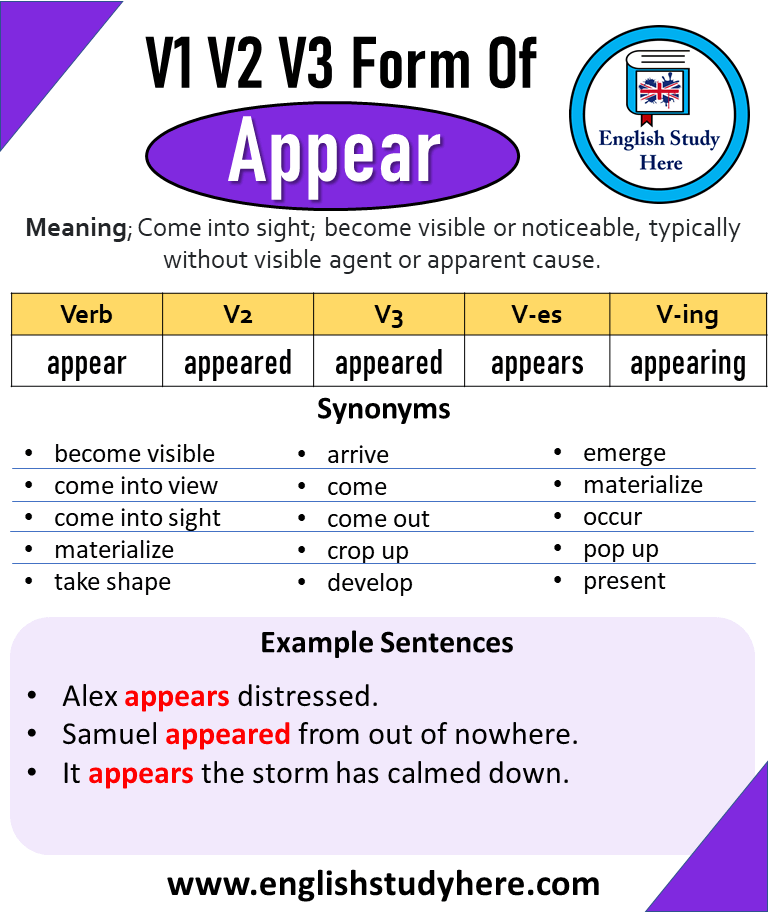
Gag Verb Forms
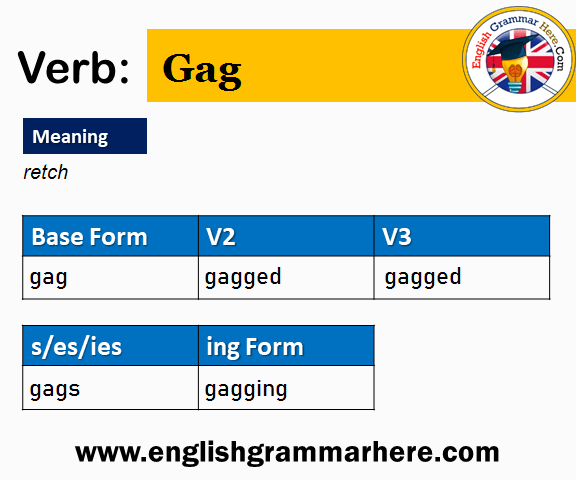
The verb “gag” can change forms. This depends on the sentence. The base form is V1: gag. The past form is V2: gagged. For past participle, it is V3: gagged. In present participle, it is V4: gagging. Finally, the third person singular form is V5: gags.
Understanding these forms helps in writing. It also aids in speaking. Knowing verb forms is important. It helps in making correct sentences. Practice these forms often. This will improve your English skills.

Credit: englishgrammarhere.com
Past And Past Participle Of Gag
Gagis a simple word. It is used in everyday talk. The past form of gag is gagged. The past participle is also gagged. Kids use it in funny stories. Adults use it too. They might say, “I gagged on food.” Or “The joke gagged me.” Gaggedmeans to choke. It can mean stopped from speaking. When someone is gagged, they can’t talk. It’s a common word. Easy to use. Easy to understand. Simple.
People use different forms of gag. They use gagging. They say, “He is gagging.” Gagging can be funny. Or serious. It depends on the story. The root form is gag. The past is gagged. The past participle is gagged. Simple, right?
Gag In Different Tenses
The simple presentform of gag is used to show action now. It is “gag” for all subjects except third person singular. For he, she, it, we use “gags”.
The simple pastform shows action that happened. We use “gagged” for all subjects. It is the same for I, you, he, she, it, we, they.
The past participleform is also “gagged”. We use it for perfect tenses. It helps in sentences like “have gagged”.
We use “will gag” for future actions. It shows what will happen later. It is used for all subjects.
The present continuousform is “gagging”. It shows action happening now. It is used with “am”, “is”, or “are”.

Credit: englishstudyhere.com
Credit: englishstudyhere.com
Conclusion
Exploring verb forms enriches understanding of language nuances. The verb “gag” illustrates this perfectly. From “gagged” to “gagging,” each form has its own role. These variations help express ideas clearly. Knowing these forms aids in writing and speaking more effectively.
Practice using them in sentences. It enhances fluency and communication skills. Remember, language is a tool for expression. Mastering verb forms ensures precise and engaging dialogue. Keep learning. Apply this knowledge in daily conversations and writing tasks. It boosts confidence and clarity.
Embrace the journey of language learning.