Point Past And Past Participle Form V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 Form of Point
Are you looking to enhance your English language skills and feel more confident in your conversations? Understanding the different forms of verbs can significantly improve your grammar and communication abilities.
One such verb that often confuses learners is “point. ” Knowing its various forms—V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5—can transform your writing and speaking. You’ll discover everything you need about the point’s past and past participle forms. By the end, you’ll not only master the use of this verb, but you’ll also gain a deeper insight into how verb forms can enrich your language usage.
Dive in, and uncover the secrets to making your English more precise and powerful!

Credit: englishgrammarhere.com
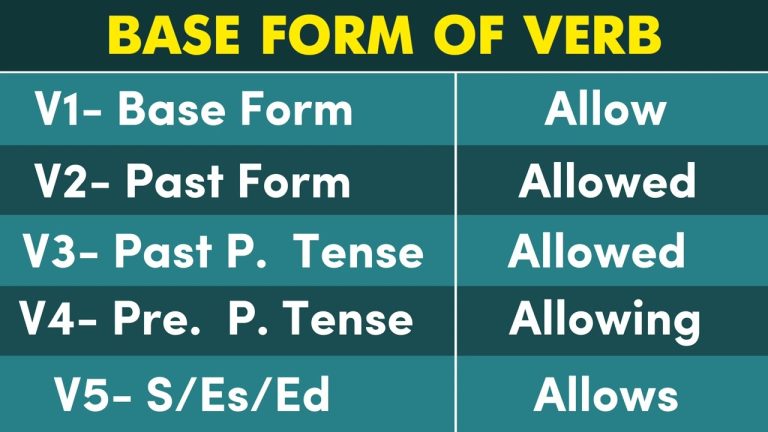
Verb Forms Of Point
The verb “point” is simple. Let’s learn its forms. The base form is point. This is the V1 form. The past simple form is pointed. This is the V2 form. The past participle form is also pointed. This is the V3 form.
Now let’s see the other forms. The V4 formis pointing. This is the present participle. Lastly, the V5 formis points. This is used with he, she, and it.
Learning these forms helps in writing. It makes sentences correct. Practice them often.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Usage Of Point In Past Tense
The verb pointchanges in the past. In the past simple form, we use pointed. This shows an action that happened before. For example, “She pointedat the map.” The past participle form is also pointed. It is used with helping verbs. Like, “He has pointedout the mistake.”
Pointing can also be in continuous forms. The present continuousform is “is pointing”. For example, “He is pointingat the board.” The present perfect continuousform is “has been pointing”. Like, “She has been pointingfor hours.” These forms show ongoing actions.
| Form | Example |
|---|---|
| V1 (Base) | point |
| V2 (Past Simple) | pointed |
| V3 (Past Participle) | pointed |
| V4 (Present Participle) | pointing |
| V5 (Present Simple) | points |
Point In Continuous And Perfect Tenses
Continuous tensesshow actions that are ongoing. The verb “point” changes as needed. In present continuous, it becomes “is pointing.” This means it is happening now. In past continuous, it changes to “was pointing.” This shows it was happening before. Future continuous uses “will be pointing.” This means it will happen later. Each tense shows a different time.
Perfect tenses show completed actions. “Point” changes to fit each tense. In present perfect, it becomes “has pointed.” This means the action is done now. Past perfect changes it to “had pointed.” This shows the action was finished before. Future perfect uses “will have pointed.” This means the action will be complete later. Perfect tenses tell when actions end.

Credit: englishgrammarhere.com
Conclusion
Understanding verb forms helps in learning English effectively. The word “point” changes in different tenses. It’s important to know them. V1 is point, V2 is pointed, and V3 is pointed. V4 is pointing, and V5 is points. These forms are essential for proper sentence structure.
Practice using them in daily conversation. It can improve communication skills. Knowing these forms aids in writing and speaking. Use this knowledge to build confidence in English. Keep practicing. Progress comes with time and effort. Stay consistent and patient in your learning journey.