Shun Past And Past Participle Form V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 Form of Shun
Are you curious about mastering English verbs and their various forms? If so, understanding the past and past participle forms of verbs like “shun” is crucial for your language journey.
Imagine speaking or writing with confidence, knowing you’ve got a firm grasp on verb forms. We’ll explore the different forms of the verb “shun” – V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5. You’ll discover how these forms are used in everyday conversation and writing.
By the end, you’ll have the tools to enhance your English skills and communicate more effectively. Dive in, and let’s unlock the potential of your language abilities together!

Credit: ltsenglish.com
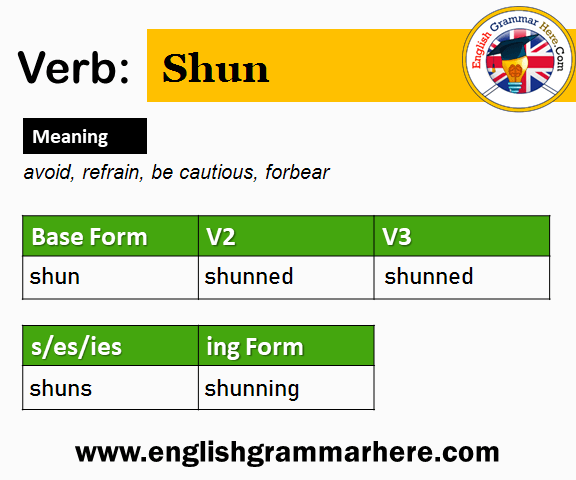
Forms Of The Verb ‘shun’
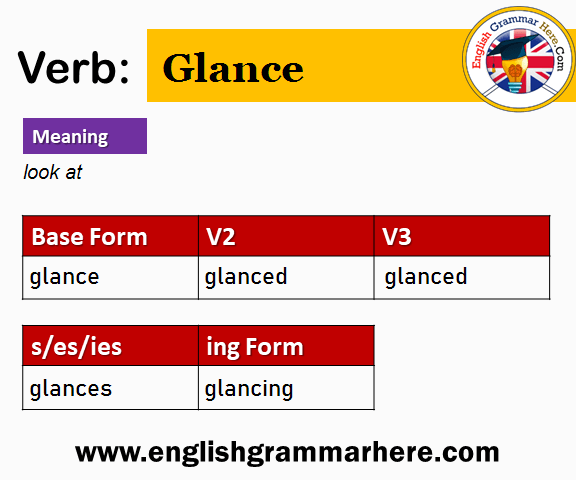
The verb ‘shun’means to avoid or keep away. It has different forms. These forms change with the tense. The base form is V1: shun. In the past, it becomes V2: shunned. The past participle is V3: shunned. In continuous tense, it is V4: shunning. The third person singular is V5: shuns.
| Form | Example |
|---|---|
| V1 | shun |
| V2 | shunned |
| V3 | shunned |
| V4 | shunning |
| V5 | shuns |
Use ‘shun’in a sentence to show avoidance. You might say, “I shunjunk food.” For past actions, use ‘shunned’. “She shunnedthe party.” In a story, use ‘shunning’to show ongoing action. “He is shunningbad habits.”
Credit: englishgrammarhere.com
Usage Of ‘shun’ In Different Tenses
The word ‘shun’ means to avoid something or someone. In the past tense, it becomes ‘shunned’. The past participle form is also ‘shunned’. These forms are used to describe actions that happened before now. For example, “She shunned the noisy crowd yesterday.” Both past and past participle forms help in storytelling.
In the present tense, ‘shun’ stays the same. It describes current actions. For example, “I shun bad habits.” In the future tense, use ‘will shun’. This talks about actions yet to happen. For instance, “He will shun junk food tomorrow.”
For continuous actions, use ‘shunning’. Like in, “They are shunning the cold weather.” The perfect form uses ‘have shunned’. It describes completed actions. For example, “We have shunned unhealthy snacks.”
Examples Of ‘shun’ In Sentences
Many people shunjunk food for better health. Some students shunnedthe noisy party and studied at home. Parents often shunTV to encourage reading. Friends shunbad habits together for a healthier life. Teachers shundistractions to focus on lessons.
Kids shunscary movies to avoid nightmares. People shunnedrisky roads during storms. Many shunsoda to drink water instead. Families shunscreen time before bed for better sleep. Adults shungossip to keep peace.

Credit: englishgrammarhere.com
Conclusion
Understanding the forms of “shun” helps in mastering English grammar. Use “shun” in daily conversations to boost language skills. The verb forms—shun, shunned, shunned, shunning—are essential in writing and speaking. Practice these forms to improve fluency and confidence. Regular usage makes learning easier.
English becomes more approachable with practice. Remember, consistency is key to progress. Keep exploring and using new words. This enriches your vocabulary and enhances understanding. Language learning is a journey. Each step brings you closer to proficiency. Stay curious and keep practicing.