Urge Past And Past Participle Form V1 V2 V3 V4 V5 Form of Urge
Unlock the secrets of mastering the English language with an intriguing dive into the verb “urge.” If you’ve ever found yourself puzzled by verb forms, you’re not alone.
Imagine effortlessly wielding the past and past participle forms of “urge” like a linguistic maestro. By understanding the different forms—V1, V2, V3, V4, and V5—you’ll gain the confidence to communicate with precision and clarity. Are you ready to elevate your language skills and impress your peers?
Keep reading as we unravel the mysteries of “urge” and empower your English proficiency.
Credit: englishstudyhere.com
Urge In Different Tenses
The word “urge” can change in different tenses. Let’s see how it works. In the present tense, we use “urge.” For example, “I urge you to read.” In the past tense, it becomes “urged.” “He urged his friend yesterday.” When talking about the past participle, it stays “urged.” “She has urged them before.” The present participle form is “urging.” “They are urging him now.” Finally, for simple future, we say “will urge.” “I will urge you tomorrow.”
Use “urge” for simple actions. In present, say “I urge him to go.” In past, “She urged him to stay.” For future, “We will urge them to try.” It’s easy to remember these forms. They help us talk about actions clearly.

Credit: englishstudyhere.com
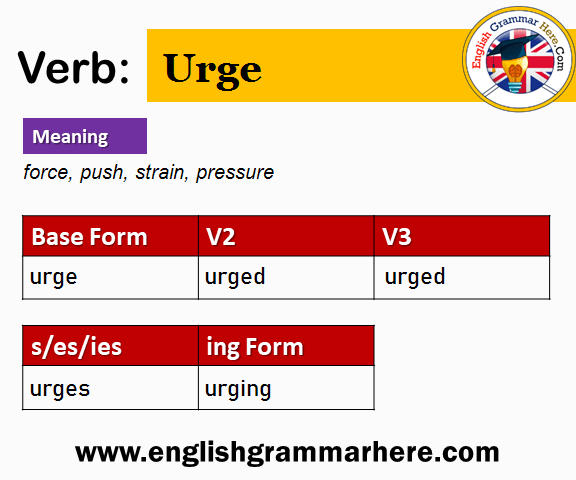
Conjugation Of Urge
The verb “urge” is used in many ways. The base form is “urge”. The past simple form is “urged”. The past participle is also “urged”. Present participle form is “urging”. The third person singular form is “urges”.
Here’s a simple table to show these forms:
| Base Form (V1) | Past Simple (V2) | Past Participle (V3) | Present Participle (V4) | Third Person Singular (V5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| urge | urged | urged | urging | urges |
Examples Of Urge Forms
Urgemeans to push someone to do something. The pastform is urged. The past participleis also urged. You can see how simple it is. For example, “She urged him to study.” Here, you see the present form. In the past, it becomes “She urged him yesterday.”
The V4form is urging. Use it in continuous tenses. “She is urging him now.” The V5form stays urgesfor third person singular. “He urges his friend every day.” Now you know all forms.
Credit: englishgrammarhere.com
Conclusion
Understanding the verb “urge” enhances English language skills. Remember the forms: urge, urged, urged, urging, urges. Practice these in sentences to improve fluency. Learning verb forms builds confidence in communication. Use this knowledge in writing and speaking. It helps convey thoughts more clearly.
Regular practice makes these forms familiar and easy. Also, it enriches vocabulary. Keep exploring and learning new words. Language learning is a continuous journey. Stay curious and keep expanding your skills. With time, you’ll find it becomes more natural. Enjoy the process of learning and growing!