Examples of Noun Clause
Have you ever found yourself tangled in the web of grammar, trying to make sense of noun clauses? You’re not alone.
Noun clauses are like the hidden gems of the English language, adding depth and detail to your sentences without you even realizing it. Imagine being able to master this element of grammar effortlessly, enhancing your communication skills and making your writing more engaging.
You’ll uncover easy-to-understand examples of noun clauses that will transform the way you view sentence structure. Prepare to dive into a world where complex grammar becomes simple, and your confidence in using noun clauses soars. Let’s unravel the mystery together.

Credit: www.yourdictionary.com
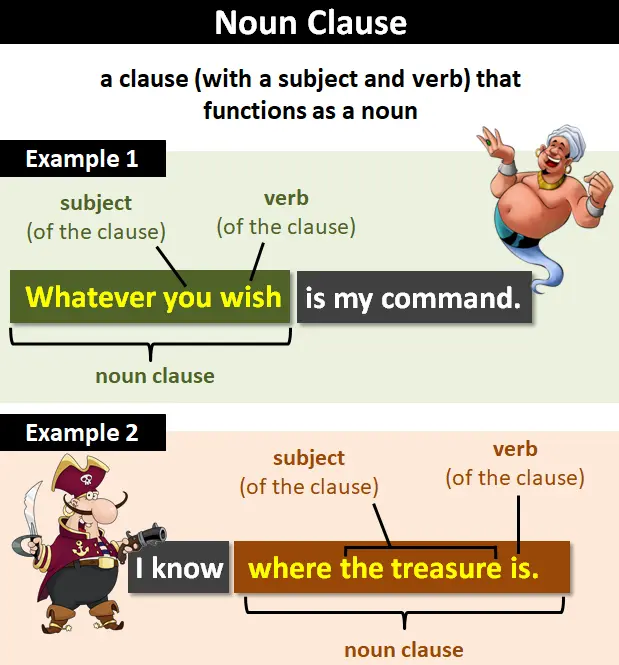
What Is A Noun Clause?
A noun clauseis a group of words. It acts like a noun in a sentence. These clauses often start with words like “that,” “what,” “who,”or “where.”They can be subjects, objects, or complements in sentences.
For example, in the sentence “I know what you did,” the clause “what you did” is a noun clause. It tells us more about the verb “know.” Another example: “She is happy that she won.” Here, “that she won” is the noun clause explaining why she is happy.

Credit: www.pinterest.com
Identifying Noun Clauses
A noun clause acts like a noun in a sentence. It can be the subject or object. For example, “What he said was surprising.” Here, the clause is the subject. Another example is “I know that she is right.” In this case, the noun clause is the object.
Noun clauses often begin with words like “that,” “what,” “who,” or “whether.” They help give more detail. “I wonder whether it will rain.” The clause adds information about the wonder. These clauses make sentences more interesting. They provide more context or clarity.
They are a key part of complex sentences. Understanding them helps in writing better. Look for clauses and their role. Practice can make understanding easier.
Noun Clauses As Subjects
Noun clauses can act as the subject of a sentence. For example, “What she said” is a noun clause. It takes the place of a noun in a sentence. “What she said is important.” Here, the clause tells us more about the subject. This helps in understanding the main point.
Authors use noun clauses to add depth to their work. A sentence like “Why he left remains a mystery” shows the subject as a noun clause. This makes the sentence interesting. It keeps readers curious. Such structures are common in stories and novels. They help build suspense and engagement.
Noun Clauses As Objects
Noun clauses can be direct objects in sentences. They answer the question “what?” or “who?” after the verb. For example, “She knows that he is coming.” The clause “that he is coming” acts as the direct object. It tells what she knows. Direct objects are important. They complete the action in the sentence.
Noun clauses can also be indirect objects. Indirect objects answer “to whom?” or “for whom?” after the verb. For example, “I told whoever was listeningthe news.” Here, “whoever was listening” is the indirect object. It shows who received the news. Indirect objects give more detail. They tell about the receiver of the action.
Noun clauses appear often in dialogue. They make sentences interesting. Example: “I wonder what he thinks.” In this sentence, “what he thinks” is a noun clause. It shows curiosity. Another example: “Tell me where you are going.” Here, “where you are going” is a noun clause. It asks for information. Noun clauses make conversations dynamic.
Noun Clauses In Apposition
Apposition is when two nouns sit side by side. One noun explains the other. This makes sentences clearer. The noun clause gives more detail. It can be short or long.
Look at this sentence: “The idea that he could flywas silly.” Here, the noun clause “that he could fly” explains “the idea.” Another example: “His belief that cats can talkamazed everyone.” The clause “that cats can talk” explains “his belief.”
Noun clauses in apposition help us understand better. They give us more information. This makes our sentences strong and clear.

Credit: easyenglishpath.com
Noun Clauses As Complements
A noun clause can be a subject complement. It completes the subject’s meaning. For example, in the sentence “The problem is that we are late,” the clause “that we are late” tells more about the problem.
Noun clauses can also be object complements. They give more details about the object. In “She called him what he wanted to hear,” the clause “what he wanted to hear” explains more about “him.”
Noun clauses are used in many statements. They add extra information. For instance, in “I know that he is coming,” the clause “that he is coming” gives more details about what I know.
Noun Clauses In Questions
Questions often use noun clausesto find answers. A noun clause can start with words like what, where, why, or how. These words make the sentence a question. For example, “What she said was funny.” The noun clause is “What she said.” It asks about the subject.
Here are some examples of noun clauses in interrogatives. “Why he left early is a mystery.” The noun clause is “Why he left early.” It asks a reason. Another example: “How she solved the puzzle amazed us.” The noun clause is “How she solved the puzzle.” It asks the method.
Common Mistakes With Noun Clauses
Noun clauses can often lead to confusion. Sometimes the meaning is not clear. This happens when the clause is not specific. For example, “He told me that he was leaving” can be unclear. Who is leaving? You must identify the subject clearly to avoid ambiguity.
Always ensure the subject is known. Use names or specific words. This helps the reader understand. Clear sentences are easier to read. They are also easier to understand.
A noun clause must have a proper structure. It needs a subject and a verb. For example, “What he wants is a mystery” is correct. But “What he wants a mystery” is wrong. The verb “is” is missing.
Always check for the verb in your noun clause. It helps the sentence make sense. A strong structure makes writing clear. It also makes it more effective.
Noun Clauses In Everyday Language
Noun clauses are words that tell more about a noun. People use them often. For example, when someone says, “I don’t know what he wants,” the words “what he wants” is the noun clause. It tells what the person does not know. These clauses make sentences clearer. They help you understand better. In conversations, noun clauses help express ideas. They make speaking easy.
Media uses noun clauses too. In a movie, a character might say, “I wonder why the sky is blue.” Here, “why the sky is blue” is the noun clause. It tells what the character wonders about. Books also use noun clauses. “The reason she left was a secret.” The words “she left” tell more about the reason. These clauses add depth to stories. They make them more interesting.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Noun Clause Example?
A noun clause is a dependent clause that acts as a noun. For example, in the sentence “I believe that honesty is important,” the clause “that honesty is important” functions as a noun, serving as the object of the verb “believe.
“
How Do Noun Clauses Function In Sentences?
Noun clauses can function as subjects, objects, or complements in sentences. For instance, in “What she said was surprising,” the noun clause “What she said” acts as the subject, providing the main focus of the sentence.
Can A Noun Clause Start With “that”?
Yes, noun clauses often start with “that. ” For example, in “She knows that he is coming,” the noun clause “that he is coming” serves as the object of the verb “knows,” providing essential information about the action.
Are Noun Clauses Always Necessary?
Noun clauses are not always necessary but provide important details. They add depth by acting as subjects, objects, or complements. For instance, “I wonder if he’ll call” uses the noun clause “if he’ll call” to express curiosity, enhancing the sentence’s meaning.
Conclusion
Noun clauses add depth to sentences. They clarify thoughts and ideas. These clauses can act as subjects, objects, or complements. Understanding them helps improve language skills. You express yourself better. Writing becomes clearer and more engaging. Practice is key. Try using noun clauses in everyday conversations.
Notice how they enhance communication. They make your sentences more interesting. Explore them further to enrich your writing. You’ll find that it becomes more dynamic. With time, using noun clauses will feel natural. Keep learning and experimenting. Your language skills will grow and evolve.